Q1. 매개효과(Mediation Effect)을 어떻게 검증할 수 있나요?
A. Mediation analysis uses the estimates and standard errors from the following regression equations (MacKinnon, 1994):
| Y = c X + e1 M = a X + e2 Y = c' X + bM + e3 |
The independent variable (X) causes the outcome variable (Y) The independent variable (X) causes the mediator variable (M) The mediator (M) causes the outcome variable (Y) when controlling for the independent variable (X). This must be true. |
1>Full Mediation: If the effect of X on Y is zero when the mediator is included (c' = 0), there is evidence for mediation (Judd & Kenny, 1981a, 1981b).
2>Partial Mediation: If the effect of X on Y is reduced when the mediator is included (c' < c)
A. To calculate the significance of the mediated effect, divide the mediated effect by its' standard error (MacKinnon & Dwyer, 1993). The regression coefficients (a, b, c, and c' from above) and the standard errors for each of those regression coefficients (sec, sea, seb, and sec' ) come from the output from running the regressions above.
-Sobel Test: Divide the mediated effect (a*b) by its' standard error.
The result is a z-score.
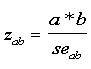
The formula for this standard error (seab) of the mediated effect (a*b) is below (Sobel 1982, 1986).
seab =![]()
Details may be found in:
-Sobel, M. E. (1982). Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. In S. Leinhardt (Ed.), Sociological Methodology 1982 (pp. 290-312). Washington, DC: American Sociological Association.
-Sobel, M. E. (1986). Some new results on indirect effects and their standard errors in covariance structure models. In N. Tuma (Ed.), Sociological Methodology 1986 (pp. 159-186). Washington, DC: American Sociological Association.
Note that there is evidence that zab is not normally distributed. There are also alternative methods to test the significane of the mediated effect.
Q3. 매개 모델에서 총 효과(Total Effect), 직접 효과(Direct Effect), 매개(간접) 효과(Mediated Effect)는 어떻게 계산하는 건가요?
A. Using the regression coefficients from the models above, the components of a mediation model are
1> Total effect = a*b + c'
The total effect is the sum of direct and indirect effects of the X on the outcome (Y).
2> Direct effect = c'
The direct effect of X on Y when taking the mediator into account.
3> Mediated(Indirect) effect = a*b
The mediated effect is also called the indirect effect. This is because it is the part of the model that indirectly affects the outcome through the mediator.
Q. 조절 효과(interaction(Moderator) effect)와 매개 효과(mediation effect) 차이가 뭐죠?
A. Mediation implies a causal sequence among three variables X to M to Y (independent variable causes the mediator and the mediator causes the dependent variable). For example, an intervention may change social norms and this change in social norms prevented smoking. An interaction means that the effect of X on Y depends on the level of a third variable. No causal sequence is implied by interaction. For example, an intervention may be successful for males but not for females--an interaction effect.
Q5. 매개 효과에 대해서 좀 더 배울 수 있는 참고 문헌이 없을까요?
A. Some good background references include:
-Baron, R.M. & Kenny, D.A. (1986). The moderator-mediator distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, Strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173-1182.
-Judd, C. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1981a). Estimating the effects of social interventions. New York: Cambridge University Press.
-Judd, C.M. & Kenny, D.A. (1981b). Process Analysis: Estimating mediation in treatment evaluations. Evaluation Review, 5, 602-619.
-MacKinnon, D.P. (1994). Analysis of mediating variables in prevention and intervention research. In A. Cazares and L. A. Beatty, Scientific methods in prevention research. NIDA Research Monograph 139. DHHS Pub. No. 94-3631. Washington, DC: U.S. Govt. Print. Office, pp. 127-153.
-MacKinnon, D.P. & Dwyer, J.H. (1993). Estimating mediated effects in prevention studies. Evaluation Review, 17, 144-158.
[출처: http://www.public.asu.edu/~davidpm/ripl/q&a.htm]


